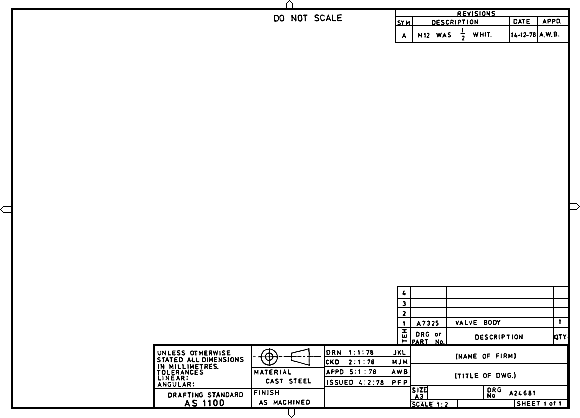
How to read technical drawings
Contents |
[edit] Introduction
The term ‘technical drawing’ has a very broad meaning, referring to any drawing that conveys the way that something functions or how it is constructed. Most drawings prepared during the later stages of the design and construction of buildings might be considered to be technical drawings.
It is important that the purpose for which technical drawings are being prepared and the people that will use them are carefully considered to ensure they are properly structured and adopt an appropriate presentational techniques. It is also important to have an understanding of how to read them.
Some of the components common to many types of technical drawing are set out below.
[edit] Border
Most drawings have a border around them. This helps ensure that the full drawing is included in reproductions.
The border sometimes includes letters and numbers to delineate zones, in the same way as a map, to help locate and pinpoint certain areas. These letters are in alphabetical order from the bottom up on the vertical axis. The numbers are in numerical order from right to left on the horizontal access. The zones are to be read from right to left.
[edit] Title block
A title block will typically appear in the bottom-right corner of a drawing and contains information related to the drawing, including:
- Name: The company or agency that prepared the drawing.
- Address: Location of the company or agency.
- Names and dates: Individuals who drew, checked and approved the drawing, and the date they did so.
- Project: The project the drawing relates to.
- Description: What the drawing is of.
- Status: What the drawing is for (eg for construction / for information).
- Drawing number: The assigned number to identify the drawing.
- Revision: Identifies the correct version of the drawing, as it may have been revised several times.
- Scale: Ratio of actual size compared to the size on the drawing / or 'do not scale' if dimensions are not to be relied upon.
- Size: The original drawing sheet size (important for determining the scale for reproductions'. See paper sizes for more information.
[edit] Revision block
A separate revision block may be located in the top-right corner of the drawing, setting out:
- The number of the revision.
- The specific changes made compared to the previous drawings.
- The date that the revisions were made.
- The approval of the revision.
[edit] Scale
It is essential to understand the size scale that the drawing has been produced to. Actual size is 1:1. Where the scale is 100:1, it means that the actual size is 100 times that shown on the drawing; the first number represents the size of the physical element, and the second number represents the drawing. It is usual that the scale will be provided in the title block.
If the dimensions of elements on the drawing are not to be relied upon, for example if the drawing is a sketch, or if responsibility for determining dimensions are with another party, the scale may be followed by the statement 'do not scale' or 'not to scale'.
[edit] Basic symbols
Architectural symbols are often used to identify common features such as topography, brickwork, doors, windows, fixtures and other elements. Understanding these, or having access to a key which notates them, will be useful in terms of interpreting the drawing.
For more information, see Symbols on architectural drawings.
[edit] Notation and units
The same notation conventions should be followed by all so that there is clear communication between different people and mistakes are avoided.
See Notation and units on drawings and documents for more information.
[edit] Circled numbers
The scale of drawings may be too small to recreate all the necessary detail. In this case, circled numbers can be added to certain parts of the drawings, which indicate that the section identified is shown in greater detail on another page.
[edit] Projections and views
Drawings generally include front, side and top of views of the object being designed. These drawings are typically drawn in either parallel or perspective projections:
- Parallel projections include orthographic drawings in which the four orthogonal views of an object are shown.
- Perspective projections are drawings in which an object is drawn using one-, two- or three-point perspective; presenting the object as three-dimensional.
For more information, see Drawing projections.
Section views may also be included which show a structure as though it has been sliced in half or cut along another imaginary plane. For more information, see Section drawing.
Exploded views may also be shown, which show how an item is assembled. See Assembly drawing for more information.
[edit] Abbreviations
Similar to circled numbers, abbreviations are used to indicate elements and instructions. Some common abbreviations used in drawings include:
- & - and
- AFF - above finished floor
- BSMT - basement
- BYND - beyond
- BOT - bottom
- CLG - ceiling
- CONT - continuous
- CPT - carpet
- DBL - double
- DEMO - demolition
- DIA - diameter
- DIM - dimension
- DN - down
- DP - depth
- DR - door
- DWG - drawing
- EA - each
- EJ - expansion joint
- EL - elevation
- ELEC - electrical
- ELEV - elevator/elevation
- EXT - exterior
- FIXT - fixture
- FLR - floor
- FND - foundation
- GA - gauge
- HI - high
- HP - high point
- HVAC - heating, ventilating and air conditioning
- INSUL - insulation
- INT - interior
- LO - low
- MECH - mechanical
- MEMBR - membrane
- MTL - metal
- NO - number
- NOM - nominal
- OC - on centre
- PLUMB - plumbing
- PLYD - plywood
- PNT - paint/painted
- PVC - polyvinyl chloride
- REQD - required
- RM - room
- SIM - similar
- SPEC - specified
- STRUCT - structure
- TO - top of
- UNO - unless noted otherwise
- U/S - underside
- VIF - verify in field
- W/ - with
For more information see Acronyms.
[edit] Find out more
[edit] Related articles on Designing Buildings Wiki
- As-built drawings and record drawings.
- Assembly drawing.
- Component drawing.
- Computer aided design.
- Concept drawing.
- Detail drawing.
- Elevations.
- Engineering drawing.
- General arrangement drawing.
- How to take off construction works.
- Installation drawings.
- Notation and units on drawings and documents.
- Paper sizes.
- Production information.
- Projections.
- Section drawing.
- Symbols on architectural drawings.
- Types of drawing.
- Working drawing.
[edit] External references
- VistaIndustrial - How to read a drawing
Featured articles and news
The Association of Consultant Architects recap
A reintroduction and recap of ACA President; Patrick Inglis' Autumn update.
The Home Energy Model and its wrappers
From SAP to HEM, EPC for MEES and FHS assessment wrappers.
Future Homes Standard Essentials launched
Future Homes Hub launches new campaign to help sector prepare for the implementation of new building standards.
Building Safety recap February, 2026
Our regular run-down of key building safety related events of the month.
Planning reform: draft NPPF and industry responses.
Last chance to comment on proposed changes to the NPPF.
A Regency palace of colour and sensation. Book review.
Delayed, derailed and devalued
How the UK’s planning crisis is undermining British manufacturing.
How much does it cost to build a house?
A brief run down of key considerations from a London based practice.
The need for a National construction careers campaign
Highlighted by CIOB to cut unemployment, reduce skills gap and deliver on housing and infrastructure ambitions.
AI-Driven automation; reducing time, enhancing compliance
Sustainability; not just compliance but rethinking design, material selection, and the supply chains to support them.
Climate Resilience and Adaptation In the Built Environment
New CIOB Technical Information Sheet by Colin Booth, Professor of Smart and Sustainable Infrastructure.
Turning Enquiries into Profitable Construction Projects
Founder of Develop Coaching and author of Building Your Future; Greg Wilkes shares his insights.
IHBC Signpost: Poetry from concrete
Scotland’s fascinating historic concrete and brutalist architecture with the Engine Shed.
Demonstrating that apprenticeships work for business, people and Scotland’s economy.
Scottish parents prioritise construction and apprenticeships
CIOB data released for Scottish Apprenticeship Week shows construction as top potential career path.
From a Green to a White Paper and the proposal of a General Safety Requirement for construction products.
Creativity, conservation and craft at Barley Studio. Book review.
The challenge as PFI agreements come to an end
How construction deals with inherited assets built under long-term contracts.
Skills plan for engineering and building services
Comprehensive industry report highlights persistent skills challenges across the sector.
Choosing the right design team for a D&B Contract
An architect explains the nature and needs of working within this common procurement route.
Statement from the Interim Chief Construction Advisor
Thouria Istephan; Architect and inquiry panel member outlines ongoing work, priorities and next steps.